Welcome, fellow explorer! Today, we are embarking on an exciting expedition through the landscape of electronics. Rest assured, there will be no complex terrains or winding roads—just the sheer excitement of unraveling the secrets behind the gadgets we use every day. Let’s hit the road!
The World Called Electronics
This is a vast and intricate world, pulsing with invisible energy that powers up everything. This energy is the result of tiny beings called electrons dancing about. The building blocks of this world are electronic components, with pathways called circuits. These circuits guide the movements of the dancing electrons. The landscape is dotted with vibrant LEDs, casting their glow on the pathways. And at the very heart of this electronic world lies the mighty microcontroller. This is a powerful artifact that empowers inhabitants (electronic components) to conjure digital spells (signals) and breathe life into circuits with a mere flicker of code.
There are different races (categories) of inhabitants of this world. The languages spoken are those of volts, ohms, and currents, and the art of soldering is a revered craft that forges connections and bridges gaps between inhabitants. You can distinguish between the races based on their functions and roles within the electronic world.
There are two major races in the electronic world. We are now going to explore these categories and identify what sets them apart. Off we go!
Active Components
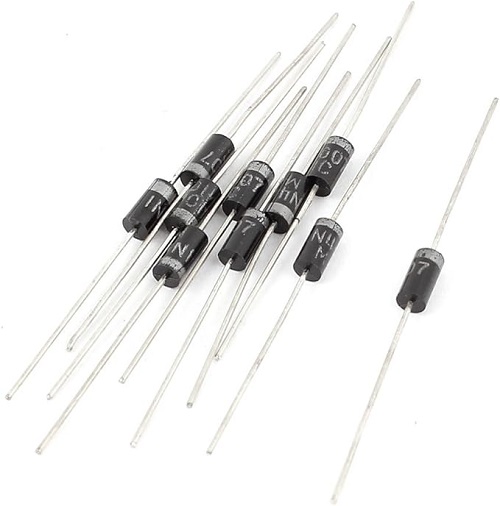
These inhabitants are energy donors. They produce energy in the form of voltage or current and deliver this energy to the circuit. They can control the flow of current (the flow of electricity that results from the movement of the tiny dancing electrons). Components that fall under the race of active components include; diodes, Integrated Circuits (ICs), MOSFETs, JFETs, optoelectronics, oscillators, and transistors.

Passive Components
This race of inhabitants are energy receivers. They store and utilize the energy delivered to the circuits by the Active Components. Capacitors, Inductors/Magnetics, Cables, Sensors, Switches, and Mechanical Devices are among the components that fall under the Passives.


Now, let’s introduce some sub-categories that are key players in the electronic community.
Semiconductors
Semiconductors are an essential component that controls and manages the flow of current. They include Transistors, Diodes, and ICs. Their functions are mainly the amplification of signals, switching, and energy conversion.

Sensors
Sensors detect stimuli such as heat, light, sound, moisture, motion, or pressure from the physical environment. They then convert the detected stimuli into an electrical signal that can be measured (quantified) and used by the electronic system.

Connectors and Cables
These are very vital in the electronic community. Connectors establish electrical connections between components, and cables transmit electrical signals between the components.


Actuators
Actuators convert energy and signals going into the electronic system to produce motion, either linearly or rotated. Linear actuators move things in a straight line, i.e., forward and/or backward. Rotary actuators revolve, so they can move things at any angle required. They can rotate at a set amount (90, 180, or 360 degrees, for example) or incrementally. Examples are Solenoids, Motors, and Speakers.

Control Components
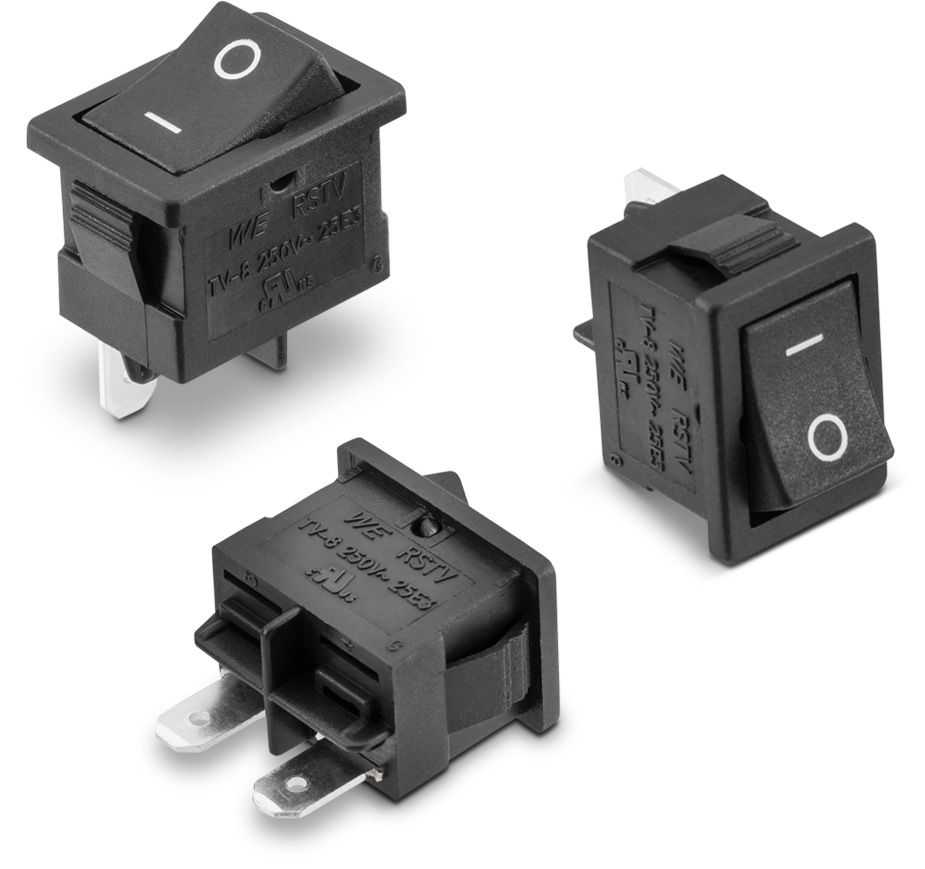
You can describe these as the police of the electronics world. Control Components regulate and manage the operations of a circuit by turning on or off the circuit. They also regulate or limit the conditions within the circuit by controlling the voltage and current. Switches, Relays and Potentiometers are some of the Control Components in the electronic community.

Frequency Control Components
For electronic systems to transmit information at a precise time and speed, Frequency Control Components provide the signals and timing controls on which they depend for the transmission. Examples of these control components are Crystals, Oscillators and Real Time Clocks (RTCs).
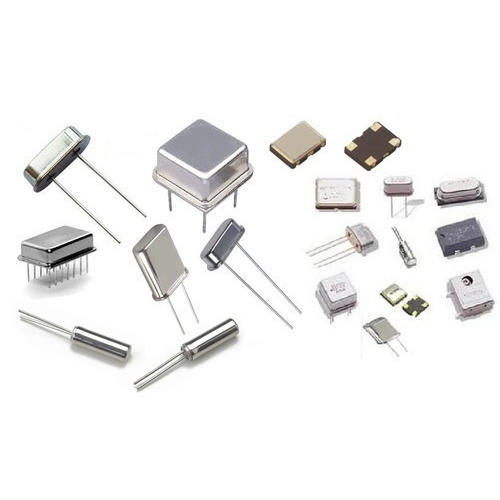
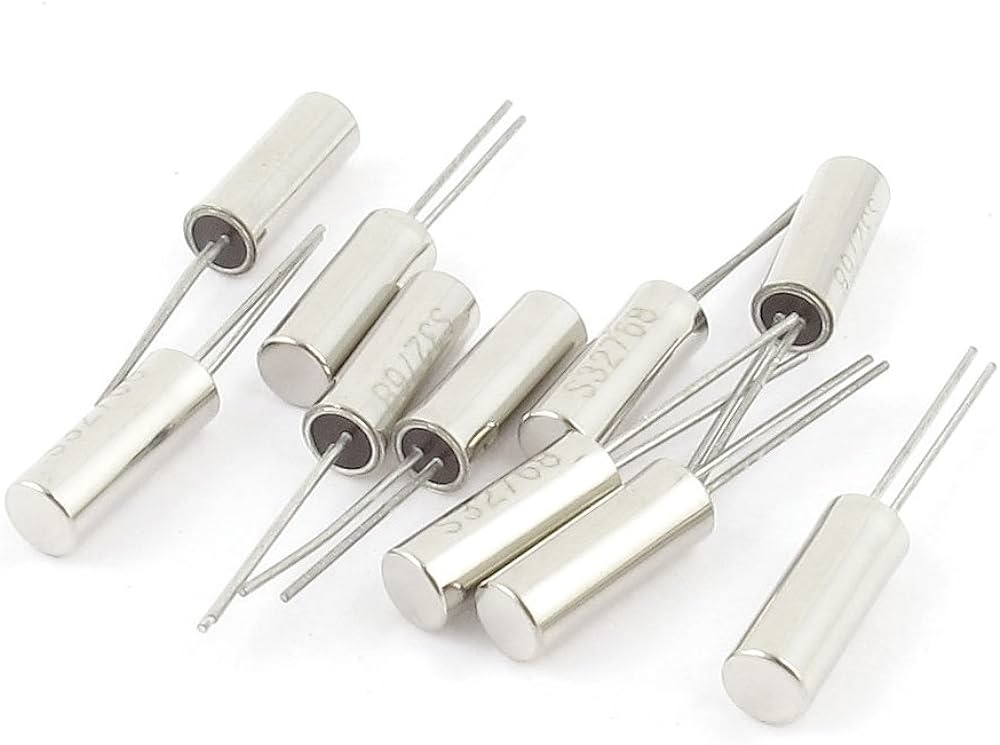


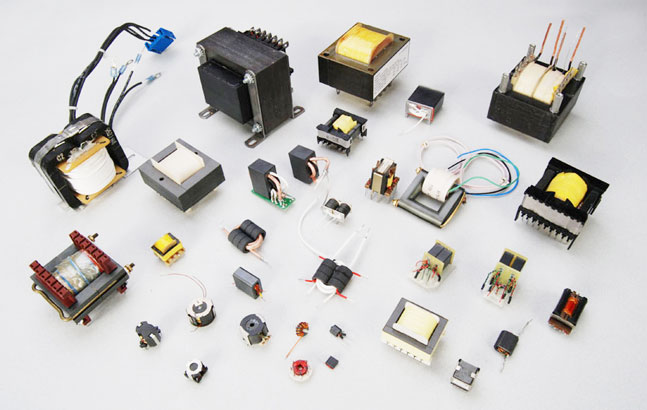
Miscellaneous Components
Just because this category is made up of an odd bunch of components doesn’t mean it is of lesser importance. Miscellaneous Components are the other essential components of the electronic system that make it complete. They perform varying vital functions in the system. Components that fall under this category are Antennas, Transformers, Fuse and Circuit breakers.

Congratulations! You have reached the end of this tour of the world of electronics. You are now a seasoned trailblazer. The next step is to embark on your own electronic adventures, armed with your newfound knowledge.
Stay tuned to this site, and we will equip you with more knowledge for your future adventures in electronics. It’s a world where every project is a quest, and every quest unveils new technological wonders—a magic that turns concepts into reality. Your curiosity is your compass, and experimentation is the key.
Until our next journey, happy exploring and stay inquisitive!



