Chemical sensors are ever-present, silently working behind the scenes to monitor our environment, protect our health, and guide our industries. These devices, like tiny detectives, detect specific chemicals and relay this information, providing valuable insights for diverse applications.
Working Principles:
Chemical sensors work by exploiting the interaction between a target analyte and a sensing element. This interaction triggers a measurable change, which can be a variation in electrical properties, optical properties, or even a physical change like mass.
Types of Chemical Sensors:
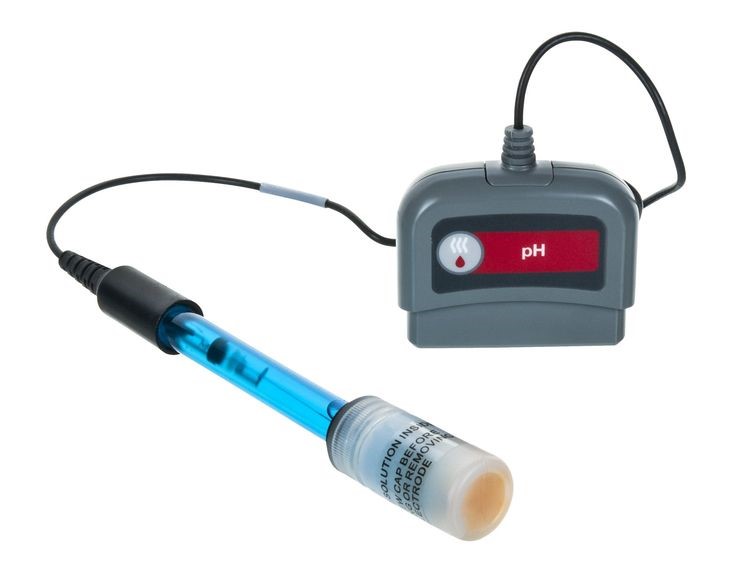
Electrochemical Sensors: These utilize the relationship between the analyte and its electrical properties. Examples include pH sensors, oxygen sensors, and glucose sensors.

Optical Sensors: These rely on changes in light absorption, emission, or scattering upon analyte interaction. Fiber optic sensors and surface plasmon resonance (SPR) sensors fall under this category.
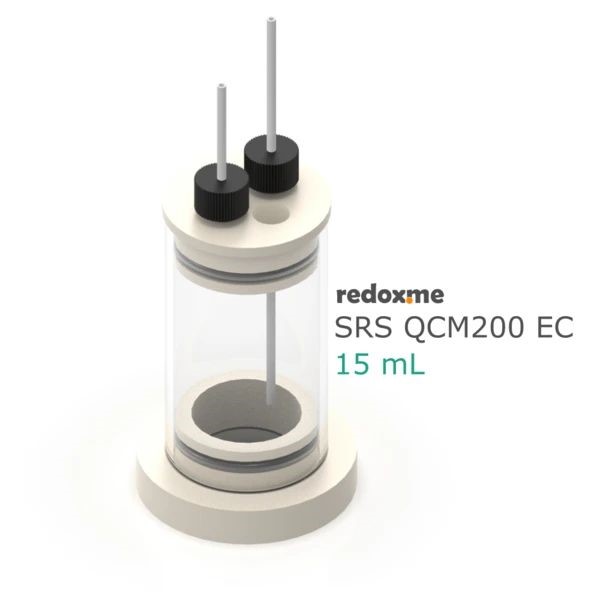
Acoustic Sensors: These detect changes in sound waves caused by the presence of the analyte. Quartz crystal microbalance (QCM) sensors are a prime example.

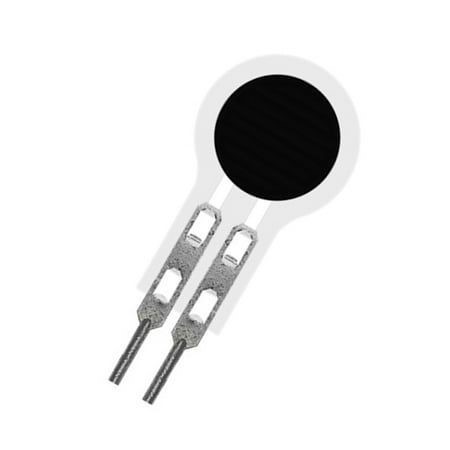
Piezoelectric Sensors: Utilizing the principle of pressure-induced electrical charge, these sensors detect mass changes caused by the analyte binding.

Applications: From Healthcare to the Environment
The diverse mature of chemical sensors empowers them to play vital roles in numerous fields:
Healthcare: Glucose sensors for diabetes management, blood oxygen sensors for monitoring patients, and even sensors for early disease detection.
Environmental Monitoring: Air quality sensors identify pollution hot spots, prompting action to improve air quality. Water quality sensors ensure clean drinking water, safeguarding public health.
Food Safety: They detect contaminants in food, ensuring the safety and quality of our food supply.
Industrial Processes: These devices monitor chemical reactions, optimize production lines, and ensure worker safety in industrial settings.
Security: Explosives and drug detectors actively safeguard our communities, preventing threats and ensuring public safety.
The Future: A World of Smart Sensors
The future of chemical sensors is bright with exciting advancements on the horizon:
Miniaturization and Integration: Tiny sensors embedded in everyday devices will provide continuous, personalized health and environmental monitoring.
Wireless Communication: Sensors connected to wireless networks will enable real-time data transmission and remote monitoring, revolutionizing data accessibility.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: AI algorithms will analyze sensor data, predicting events, optimizing processes, and providing early warnings.
Chemical sensors are not just passive observes; they are active agents, shaping a safer, healthier, and more efficient world. As these intelligent devices continue to evolve, they will play an increasingly crucial role in addressing global challenges and building a sustainable future.
Some of our available chemical sensors available in our Shop:



