Imagine a world without smartphones, computers, or even basic electrical appliances. It’s hard to fathom, yet this is the world we would live in without the invention of the “transistor”. This small, unassuming semiconductor device is the bedrock of modern electronics, responsible for revolutionizing our lives in ways we can barely comprehend.
What is a Transistor?
Transistors are semiconductor devices that act as electronic switches, controlling the flow of electricity. It’s a fundamental building block of modern electronics, enabling the creation of complex circuits and devices like computers, smartphones, and countless others. Transistors have revolutionized electronics and continue to drive innovation. Here’s a breakdown of historical development and modern applications.
HISTORICAL KNOWLEDGE
The “transistor effect” was discovered by John Bardeen, Walter Brattain(research scientists) and William Shockley(physicist) in 1947 at Bell Labs. This involved controlling the flow of electricity through a semiconductor material using a small electric signal. This paved the way for the development of the first transistor.
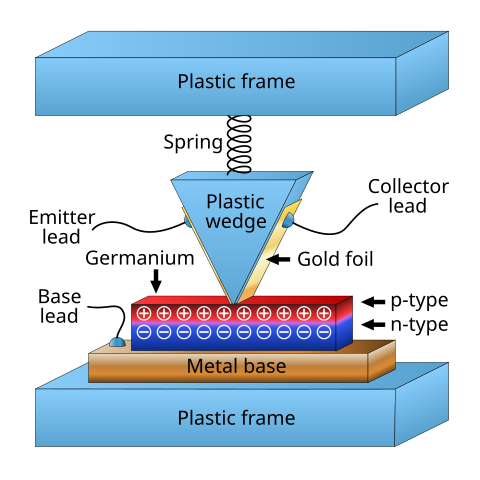
I’m sure you’re interested in knowing how the first working transistor came about. The first working transistor is known as a Point-Contact Transistor. Here’s a deeper dive:
What is a Point-Contact Transistor?
The point-contact transistor consists of a semiconductor material (typically germanium in the early days) with two fine metal “whiskers” (thin wires) pressed against its surface. The whiskers act as the emitter and collector, while the semiconductor material acts as the base. Point-contact transistors were the first type of transistor to be successfully demonstrated. They played a crucial role in proving the “transistor effect” and were initially used in a range of early electronic circuits.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Point-Contact Transistors
Advantages:
- Simple Structure: They were relatively simple to fabricate.
- Early Success: They were the first working transistors, which allowed for rapid advancement in electronics.
Disadvantages:
- Low Reliability: The mechanical contact between the whiskers and the semiconductor material was unreliable, prone to changes over time.
- High Noise Levels: The point-contacts introduced significant noise into the signal, making them unsuitable for many applications.
- Limited Power Handling: They could handle only small amounts of power.
Point-contact transistors, despite their limitations, found several important applications in the early days of semiconductor technology:
Early Radios
**Amplification:** Point-contact transistors were used in the first transistor radio, replacing bulky and inefficient vacuum tubes for amplifying radio signals. These radios were smaller, more portable, and consumed less power, marking a significant advancement in radio technology.
Hearing Aids:
**Miniaturization:** Point-contact transistors were crucial in miniaturizing hearing aids. They allowed for smaller, more discreet devices that could be worn comfortably, significantly improving the lives of individuals with hearing impairments.
Early Computers:
**Logic Gates:** Point-contact transistors were used in early computers for creating simple logic gates (AND, OR, NOT) that formed the basis of computation. However, their unreliability limited their use in complex computer systems.
Other Applications:
**Early Telephones:** They were used in early transistorized telephones, improving the quality and reliability of voice transmission.
**Military Devices:** Point-contact transistors were employed in early military communication and radar systems due to their ability to withstand harsh environments.
While point-contact transistors had a short lifespan in mainstream electronics, their historical significance cannot be overstated. They:
**Proved the Transistor Effect:** Their success validated the concept of controlling current flow in semiconductors, making way for the development of modern transistors.
**Enabled Early Innovations:** They facilitated significant advancements in radio, hearing aids, and early computers, laying the foundation for the semiconductor revolution.
While their direct applications are now largely obsolete, the point-contact transistor holds a special place in the history of electronics as an evolving innovation that ushered in the era of semiconductor-based technology.

We now know how the first working transistor (Point-contact transistor) was discovered but they had limitations which later on brought about a new significant discovery Junction Transistors.
Why they were Replaced:
You’re curious about junction transistors! It’s a fascinating topic, and the junction transistor is considered a pivotal invention that revolutionized electronics. Let’s dive into its discovery:
**Shockley’s Vision:** William Shockley, one of the inventors of the point-contact transistor, envisioned a device that used a semiconductor junction- a boundary between different types of semiconductor materials- to control the flow of current.
**The Shockley Diode:** William Shockley, working at Bell Labs, first proposed the “Shockley Diode,” which used a p-n junction(a junction between a p-type and n-type semiconductor) for rectification.
**The Breakthrough:** Building on the diode concept, William’s team successfully built the first junction transistor in 1951. This device utilized a p-n-p or n-p-n configuration, where two junctions were created within a semiconductor crystal.
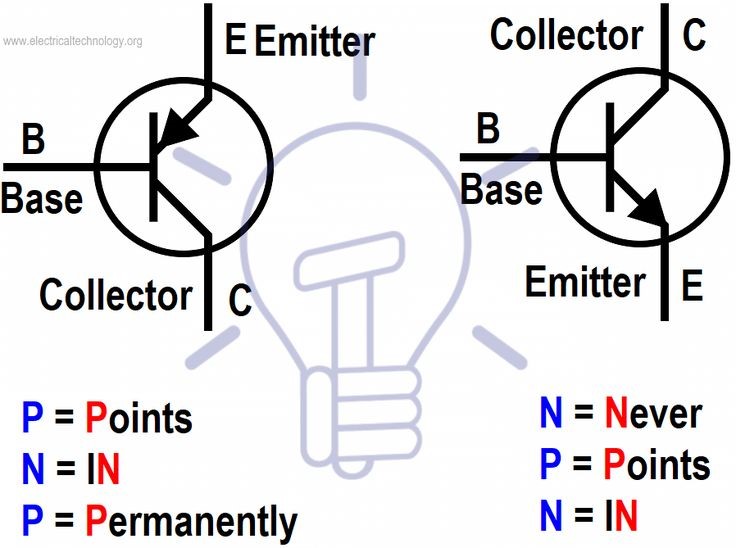
A transistor consists of three layers:
**Emitter:** Releases electrons into the base.
**Base:** Controls the flow of electrons from the emitter to the collector.
**Collector:** Collects the electrons from the base.
There are two basic types of junction transistors:
- P-N-P: This type has a p-type emitter and collector, with an n-type base sandwiched between them.
- N-P-N: This type has an n-type emitter and collector, with a p-type base in the middle.
Advantages
- High Reliability: The well-defined junctions of junction transistors make them incredibly robust and reliable, unlike the point-contact transistors.
- Low Noise Levels: The junctions minimize noise, resulting in cleaner signals.
- Efficient Current Amplification: Junction transistors can amplify currents effectively, enabling them to drive larger loads.
- Easy Fabrication: Their structure allows for mass production, driving down costs and making electronics more accessible.
- Versatility: They can be used in a wide variety of circuits, including amplifiers, oscillators, and switches.
There are two main types of transistors:
**Bipolar Junction Transistors (BJTs):** The most common type of junction transistor. Utilizes a small current at the base to control a larger current flowing between the emitter and collector. They are used in a vast range of applications, from amplifiers to switching circuits.
**Field-Effect Transistors (FETs):** These transistors use an electric field to navigate the current flow. They are often preferred for their high input impedance and low noise levels, making them suitable for applications like amplifiers and sensors.
How Transistors Work:
- BJTs: A small current at the base controls the flow of a larger current between the emitter and collector. Think of it like a valve controlling the flow of water in a pipe.
- FET: An electric field applied to the gate controls the flow of current between the source and the drain. Imagine it like a gate controlling the flow of water through a channel.
The Application of Transistors:
The impact of transistors on our lives is immense. They are the building blocks of virtually all modern electronics, powering everything from our smartphones and computer to medical equipment and automobiles.
Here are some key applications:

**Computers:** They are the foundation of microprocessors, which control the functionality of computers.
**Sensors and Actuators:** They play a crucial role in sensing physical phenomena like temperature, light, and pressure and are used in actuators to convert electrical signals into physical movement.
**Mobile Devices:** They power the processors, memory, and communication circuits in smartphones, tablets, and laptops.
**Medical Equipment:** Transistors are used in medical devices such as pacemakers, hearing aids, and MRI machines. Their ability to amplify and control signals is critical for the diagnosis and treatment of various medical conditions.
**Automotive Industry:** Transistors are widely used in automobile for controlling engine functions, braking systems, and other crucial components. Their ability to switch and amplify signals is crucial for ensuring safe and efficient vehicle operation.
Transistors have revolutionized electronics, leading to the creation of countless innovations that have shaped our world. From the tiny computers we carry in our pockets to the vast communication networks that connect us globally, transistors have left an inerasable mark on our lives.
This brings us to the end of how transistors came into existence or was discovered , different types of transistors and their modern applications. Let me know if you’d like more information on a specific aspect of transistors or have other questions about their history or applications.
Until next time, it’s bye 🙂
Visit our online shop – Any Component Lab and start experimenting with this essential component in your next project!
Our various transistor components;
… and many more!